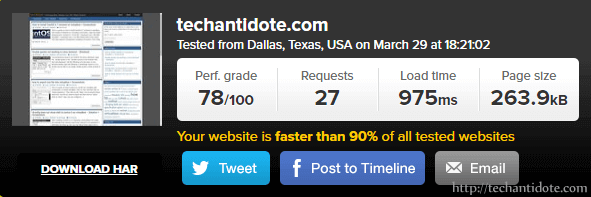
Step 1. Perform a speed test
Go to https://tools.pingdom.com and enter your website to test your current load time. This is to get a idea the load time and performance score for reference.
Step 2. Configure Cloudflare CDN for your wordpress
You can configure cloudflare CDN for your wordpress website for free which will reduce latency and hence improve page load speeds. Create an account at http://www.cloudflare.com and change your name servers to the ones provided by cloudflare. For a more detailed guide with screenshots on how to configure cloudflare CDN for your website, you can find it here. (Link opens in new tab)
Step 3. Optimize your images
If your wordpress blog has a ton of images, then its best you optimize them so that your blog would load faster. You can either use plugins such as ‘WP Smush‘ (Plugin Link) or “Compress JPEG & PNG images” (Plugin Link) to optimize images. You can also manually optimize it and upload them if your an expert.
I also did notice that if the image are of .PNG format, then its best to use Tiny PNG (https://tinypng.com) or use their plugin “Compress JPEG & PNG images” as it is more efficient than ‘WP Smush’.
Step 4. Remove Google Fonts
If your theme loads google fonts, you may find few requests going out to the google server which can slow down your site. Disabling it is easy and all you have to do is install plugin named ‘Remove Google Fonts References‘.
Step 5: Disable Gravatar Hoovercards
This step is only needed if you have installed and configured Jetpack for your wordpress blog.
Go to your wordpress dashboard, click on Settings>Discussion. Uncheck the option “View people’s profiles when you mouse over their Gravatars” next to “Gravatar Hovercards”.
If ‘Gravator Hovercards’ section is greyed out, then click on “Shows Avatars”, uncheck “View people’s profiles when you mouse over their Gravatars” and then uncheck “Shows Gravatar” and save changes.
Step 6. Remove query strings from static resources
This have a huge impact on your performance score in pingdom and Gtmetrics. I have written an article on how to remove query strings from static resources to improve load times here. (Link opens in new tab)
Step 7. Remove unwanted plugins
Like the title suggests, if you don’t use a plugin its best to remove them.
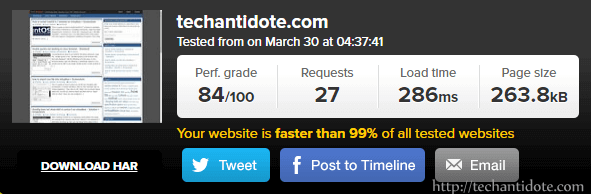
Once done, re-run the speed tests https://tools.pingdom.com to compare before and after performance results.
Sources: Link



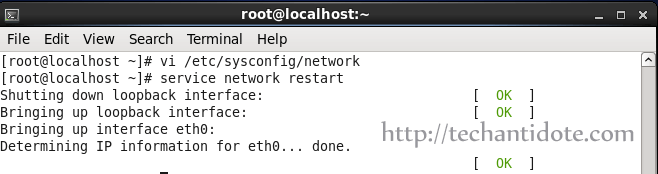
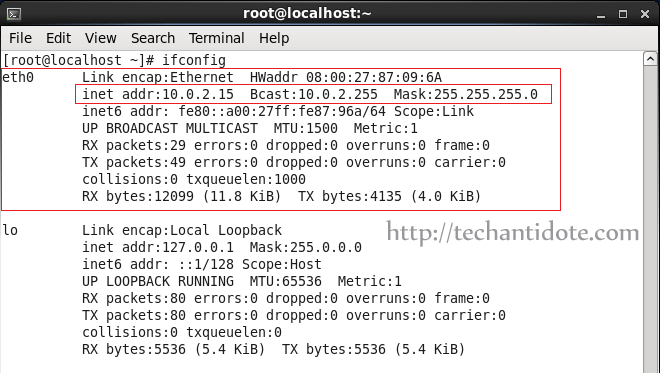
 To edit your network file, type the following command:
To edit your network file, type the following command: